Related Topic
Cleaning and Disinfection Program for Breeder Flocks ( with disinfectant's doses)
Best Practices for Cleaning download pdf here
The Chicken House
Overview
General overview of
C&D
·
Detailed review
·
Darkling beetle infestation
·
Rodent infestation
·
Water, a source of
infection
The Objective
To clean and disinfect
the poultry house so that all potential poultry and human pathogens are removed
and to minimize the numbers of residual bacteria, viruses, parasites and
insects etc. between flocks minimizing any effect on health, welfare and
performance of the subsequent flock.
Clean out Stages
1. Planning 2. Depletion
3. Insecticide application 4. Rodent control
5. Remove
dust 6. Pre-soak
7. Remove
equipment 8. Remove
litter – litter disposal
9. Cleaning of water lines 10. Reapply
insecticide
11. Sweep 12. Washing
13. Drying 14.
Disinfection
15. Reapply insecticide 16.
Fumigation
17. Rodent control
Planning
Depletion
“Simply culling of breeders flock after the age of 64
weeks “
Darkling Beetles and Disease
• IBDV, MDV • NDV and
AIV
• Reo
viruses, ILT, Fowl Pox • Salmonella
• Campylobacter • E. coli
• Aspergillus, Staphylococcus • Coccidia
• Roundworms • Fowl
tapeworm
Facts Facts
• Average
beetle size (≈6mm long, 100mg)
· Assuming
beetles convert feed as well as
broilers; bug load could cost 1 point of FCR
• In a
complex killing 1 million birds/week, 1 point of FCR can cost up to an estimated $300,000/year
Life Cycle
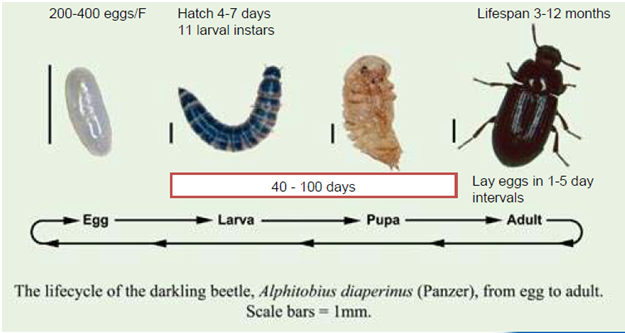 |
| Life cycle of darkling beetles |
Effective darkling beetle control program
• Identify
darkling beetle infestation
• Keep
litter moisture low (key nutrient for
larvae and beetles).
• Regular
maintenance of water lines will prevent leaking and will help reduce beetle numbers.
• Use a
pesticide that is suitable for the type and location of treatment.
Follow label instructions
for application procedures and rates.
• Rotate
insecticides and the use of boric acid.
• Treat
within 24 to 48* hours after birds are removed from the house.
• Apply
treatments in a manner that can reach beetles and larvae that may be several inches under the litter. Use the highest permitted rate.
application and only mix it within a 2 to 3 inch depth.
Alphitobius diaperinus
 |
Controlling Alphitobius diaperinus
In Broiler Houses
• Trials
were conducted during one year under field conditions
• Tested
combined treatment
— Adulticide
– cyfluthrin [sī-floo-thrǐn]
— Larvicide
- triflumuron [trī-floo-mūrǒn]
• The
combined insecticide treatment greatly reduced the adult and larval stocks throughout
the different broiler growing periods, and control of A. diaperinus populations was achieved by the end of the
second
Darkling Beetles Eat Feed
·
There can
be up to 2 million darkling beetles and larvae in a broiler house
·
Average
beetle size (≈6 mm long, 100 mg) and assuming beetles convert feed as well as
broilers; bug load could cost 1 point of FCR
·
In a
complex killing 1 million birds/week, 1 point of FCR can cost up to an
estimated $300,000/year
Rodent Control
Estimating Rat Populations
• Rule of thumb:
—If you don’t see rats but see signs of them, there are ~1 to
100
—If you see them occasionally at night, there are ~100 to 500
—Occasional daytime and numerous night sightings indicate ~400
to 1,000
—Seeing several in the daytime may indicate a presence of as
many as 5,000.
Fill Gapes
Cats and Dogs Can Carry
Pathogens
• Physical vector
• Pasteurella• Salmonella
• Others…H5N1• Swine dysentery (Brachyspira ssp.)
Pre Spray
• Sprayer
or low pressure washer
• Ceiling
to floor
• Dampen down
dust
Remove Equipment
• Frames/Nest Boxes
• Supplementary
Equipment
• If it can’t be wet
Cleaned or removed-
Dry clean and cover it up!
• Environmental sensors etc!
Remove Litter
• Remove
all litter and debris
• Final dry
brush of floor
• Avoid
windy weather
• Use
covered trailers
• Disinfect wheels
Litter Disposal
• > 2 km
from the farm
• Method of
disposal
— Spread
and ploughed in arable land
— Landfill
— Composting
— Incinerating
• Follow
government regulations
— Traceability
— Nitrites
— Nitrates
Washing
Internally and Externally
• Pressure
washers-
100 bar min
• Preferably
hot water > 40oC
• Suitable
Chemicals
• Interactions
• Aluminum
houses- Foam Detergent
• Wood-Traditional
Detergent
• Correct
Dilution rates
• The
correct sequence
Dilution Ratio Table
Water in liters
|
0.5
|
1
|
2
|
5
|
10
|
Dilution ratio
|
|||||
Dilution Ratio
|
|||||
1:20
|
25ml
|
50ml
|
100ml
|
250ml
|
500ml
|
1:40
|
13ml
|
25ml
|
50ml
|
125ml
|
250ml
|
1:50
|
10ml
|
20ml
|
40ml
|
100ml
|
200ml
|
1:60
|
8ml
|
16ml
|
33ml
|
83ml
|
166ml
|
1:80
|
6ml
|
13ml
|
25ml
|
63ml
|
125ml
|
1:100
|
5ml
|
10ml
|
20ml
|
50ml
|
100ml
|
1:150
|
3ml
|
7ml
|
13ml
|
33ml
|
67ml
|
1:200
|
3ml
|
5ml
|
10ml
|
25ml
|
50ml
|
Sequence
- From apex to downwards
- Start at the rear of the house and move to the front
- Pay attention to cracks and joints
Washing Stages
• Detergent
• Rinse
• Excess
water collected
• Visual
Check
Poultry Water Line Cleaning:
Overrated or Underappreciated?
“The evidence is growing that water
sanitation can be a crucial tool in addressing
poor poultry flock performance”
When the poultry
industry advanced from open drinkers and troughs to enclosed nipple lines, it
was the perfect solution to both labor and contamination challenges. Yet the
test of times has proven that while enclosing water supply in a poultry barns
has greatly improved water sanitary qualities, it has not eliminate the risk of
disease challenges.
Bio film Slime
• Poor line
sanitation _ bio film
• Bio film
lives on very little nutrients
• Can cause
health challenges, flock after flock
• Disease
agents like E. coli and Salmonella
— Salmonella may be
isolated from 7 to 8% of water samples collected from nipple drinker systems.
• Once
established is 10-1000x harder to remove
• Can
return in 2-3 days after cleaning
— When we
do a poor job of cleaning
— When we
don’t keep water sanitized
— When we
add food supply
What Influences Bio-films?
• Natural
contaminants Iron, manganese,
sulfur
• Vitamins • Electrolytes • Organic
acids
• Sugar
water • Vaccines
and vaccine stabilizers
• Probiotics
and Antibiotics • Do you
clean lines after product use?
• How often
is water sanitation?
sacrificed so water can be delivery route for products?
Water System
• Drain pipes and
tanks • Flush
lines
• Cleanse
header tanks • Scale /
bio film removal
• Refill
tanks and add sanitizer • After
4-24hrs remove solution
• Rinse with
fresh water
• Run sanitizer solution through lines (check no air locks)
Feed System
• Ensure bulk bins and augers are free of feed
• Dry brush
• Do not introduce water to the bulk bins!!
• Wash and disinfect pans, tracks, auger pipes etc
Repairs and Maintenance
• Prior to
final disinfection
• Gas and
electrics
• Buildings
and Equipment
• Concrete
Repairs
• Vermin
proofing
• Wild bird
proofing
• Clear
Drains
Disinfection
• Only when
buildings are internally and externally clean
• Repairs
are complete
• No
organic matter
• Correct dilution
rates
• Remember
the sequence
Fumigation Monitoring Effectiveness
• Damp
Surface (not puddles) • TVC’s
Total Viable Counts
• Seal
house tight • Salmonella
• Warm
house to 21oC (70RH) • Set
Standards
• Seal gas
in house for 24 hrs • Monitor
Trends
Summary
• Adopt,
develop standard operating procedures
• Clean and
disinfect after every flock
• Monitor
effectiveness
• Darkling
beetles and rodents are potential sources of Salmonella, etc.
• Water is
often neglected
• Allow
adequate down time between
Related Topic
Cleaning and Disinfection Program for Breeder Flocks ( with disinfectant's doses) 











4 comments:
I know your expertise on this. I must say we should have an online discussion on this. Writing only comments will close the discussion straight away! And will restrict the benefits from this information.
הרחקת יונים
This article is very interesting and helpful. Thank you for sharing! If you have any difficulties in cleaning difficult dirt, you can use water blaster. Water blaster can help you clean anything faster and easier.
I wanted to thank you for this excellent read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you bookmarked your site to check out the new stuff you post Vivo Y15 Price In Pakistan
Really thanks to everyone one
Post a Comment